The Vertical Diet was created by renowned sports nutritionist Stan Efferding. It is a dietary approach that emphasizes nutritious, nutrient-dense foods, prioritizing digestive health and optimizing physical performance.
Table of Contents
The Vertical Diet is a nutrition plan that has gained popularity among athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Developed by Stan Efferding, a professional bodybuilder and powerlifter, the diet focuses on consuming nutrient-dense foods to fuel the body and optimize performance. The diet is designed to be sustainable and flexible, allowing individuals to customize it to their specific needs and preferences.
At its core, the Vertical Diet emphasizes the importance of consuming a variety of whole foods, including lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. The diet also emphasizes the importance of adequate hydration and electrolyte balance, as well as the use of supplements to support optimal health and performance. The Vertical Diet is designed to promote satiety and reduce cravings, making it easier to adhere to over the long term.
While the Vertical Diet has been praised by many for its effectiveness in improving athletic performance and overall health, it is important to note that it may not be suitable for everyone. As with any diet, individuals should consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to their eating habits.
Fundamentals of Vertical Diet
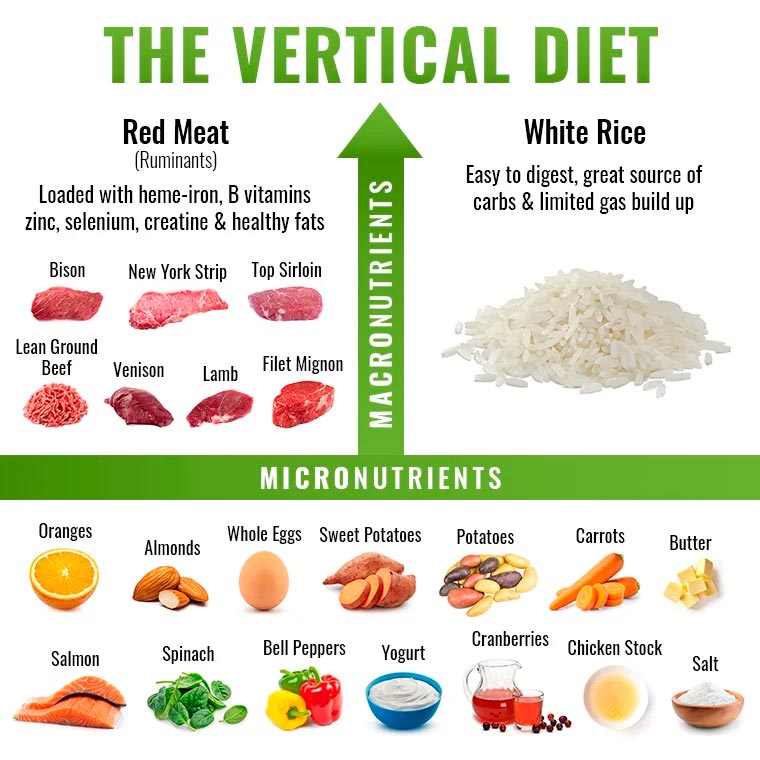
Vertical Diet is a nutrition plan that emphasizes the consumption of whole foods and micronutrients to support optimal health and performance. It was developed by Stan Efferding, a world-renowned powerlifter and nutrition coach, and has gained popularity among athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
The Vertical Diet consists of a few fundamental principles that are designed to provide the body with the nutrients it needs to function optimally. These principles include:
1. Focus on whole foods
The Vertical Diet emphasizes the consumption of whole, nutrient-dense foods such as lean meats, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products. These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients that support overall health and performance.
2. Prioritize micronutrients
Micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, are essential for optimal health and performance. The Vertical Diet emphasizes the consumption of foods that are rich in these micronutrients, such as leafy greens, berries, and organ meats.
3. Manage digestion
The Vertical Diet includes foods that are easy to digest, such as white rice and lean meats, to help minimize digestive stress and maximize nutrient absorption.
4. Optimize hydration
Proper hydration is essential for optimal health and performance. The Vertical Diet emphasizes the consumption of water and other hydrating fluids, such as coconut water and bone broth.
5. Individualize for specific needs
The Vertical Diet is highly individualized and can be tailored to meet the specific needs of each individual. It takes into account factors such as body composition, activity level, and food intolerances to create a personalized nutrition plan.
Overall, the Vertical Diet is a nutrition plan that emphasizes the consumption of whole foods and micronutrients to support optimal health and performance. By following the fundamental principles of the Vertical Diet, individuals can create a nutrition plan that is tailored to their specific needs and goals.
Benefits of Vertical Diet

Nutritional Benefits
The Vertical Diet is a nutrition plan that emphasizes nutrient-dense foods that provide the body with essential vitamins and minerals. This diet includes a variety of meats, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains to ensure that the body gets all the nutrients it needs. The diet also encourages the consumption of fermented foods, which are rich in probiotics that promote gut health.
Weight Management
The Vertical Diet is designed to help individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight. The diet emphasizes nutrient-dense foods that are low in calories, which can help individuals feel full and satisfied while consuming fewer calories. The diet also encourages the consumption of protein, which can help individuals build and maintain muscle mass, which in turn can help boost metabolism and burn more calories.
Digestive Health
The Vertical Diet is designed to promote digestive health by including foods that are easy to digest and rich in fiber. The diet encourages the consumption of fermented foods, which can help promote the growth of healthy gut bacteria. The diet also includes foods that are low in FODMAPs (Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols), which can help reduce symptoms of digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
In summary, the Vertical Diet is a nutrition plan that emphasizes nutrient-dense foods, promotes weight management, and supports digestive health. By following this diet, individuals can ensure that their body is getting all the essential nutrients it needs while maintaining a healthy weight and promoting digestive health.
Components of Vertical Diet
The Vertical Diet is a nutrition plan that emphasizes nutrient-dense foods to support optimal health and athletic performance. The diet is based on a few key components, including protein sources, carbohydrate sources, and fat sources.
Protein Sources
Protein is an essential macronutrient that is necessary for muscle growth and repair, as well as many other physiological processes. The Vertical Diet emphasizes high-quality protein sources, such as:
- Grass-fed beef
- Wild-caught fish
- Free-range chicken
- Eggs
- Low-fat dairy products
These protein sources are rich in essential amino acids and other nutrients that support muscle growth and recovery.
Carbohydrate Sources
Carbohydrates are an important source of energy for the body, and the Vertical Diet emphasizes the use of nutrient-dense carbohydrate sources. These include:
- Rice
- Potatoes
- Sweet potatoes
- Fruits
- Vegetables
These carbohydrate sources are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which help to support overall health and athletic performance.
Fat Sources
Fat is another important macronutrient that is necessary for many physiological processes, including hormone production and brain function. The Vertical Diet emphasizes the use of healthy fat sources, such as:
- Avocado
- Olive oil
- Coconut oil
- Nuts and seeds
- Fatty fish
These fat sources are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and other nutrients that support optimal health and athletic performance.
Overall, the Vertical Diet emphasizes the use of nutrient-dense foods to support optimal health and athletic performance. By focusing on high-quality protein sources, nutrient-dense carbohydrate sources, and healthy fat sources, individuals following the Vertical Diet can ensure that they are getting the nutrients they need to support their goals.
Meal Planning in Vertical Diet

Meal planning is a crucial part of the Vertical Diet. The goal is to ensure that the diet is balanced and provides all the necessary nutrients. The diet is based on the consumption of whole foods, which makes meal planning easy and straightforward.
The first step in meal planning is to determine the daily calorie needs. This can be done using an online calculator or consulting with a nutritionist. Once the calorie needs are determined, the next step is to divide them into meals. The Vertical Diet recommends consuming four to six meals per day, depending on the individual's needs.
The next step is to determine the macronutrient ratio. The Vertical Diet recommends a ratio of 50% carbohydrates, 25% protein, and 25% fat. However, this can be adjusted based on individual needs and preferences.
When planning meals, it is important to focus on nutrient-dense foods. The Vertical Diet recommends consuming a variety of animal proteins, such as beef, chicken, fish, and eggs. It also recommends consuming a variety of fruits and vegetables, such as spinach, kale, broccoli, berries, and citrus fruits. Starchy carbohydrates, such as rice, potatoes, and sweet potatoes, are also recommended.
To make meal planning easier, the Vertical Diet provides a list of recommended foods. This list includes:
- Grass-fed beef
- Wild-caught fish
- Free-range chicken
- Whole eggs
- Spinach
- Kale
- Broccoli
- Berries
- Citrus fruits
- Rice
- Potatoes
- Sweet potatoes
In conclusion, meal planning is an essential part of the Vertical Diet. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods and following the recommended macronutrient ratio, individuals can ensure that they are consuming a balanced diet that provides all the necessary nutrients.
Potential Drawbacks
Limited Variety
One of the drawbacks of the vertical diet is that it may limit the variety of foods that individuals can consume. This is because the diet emphasizes certain foods over others, such as red meat and white rice. While these foods can provide important nutrients, consuming them in large quantities may lead to boredom or dissatisfaction with the diet.
In addition, the emphasis on specific foods may make it difficult for individuals to eat out or socialize with others who do not follow the vertical diet. This can lead to feelings of isolation or difficulty adhering to the diet in social situations.
Potential Nutrient Deficiencies
Another potential drawback of the vertical diet is that it may lead to nutrient deficiencies if not followed properly. For example, the diet emphasizes red meat as a source of iron, but individuals who do not consume enough red meat may be at risk for iron deficiency anemia.
Furthermore, the diet may not provide enough variety in fruits and vegetables, which are important sources of vitamins and minerals. This can lead to deficiencies in nutrients such as vitamin C, vitamin A, and potassium.
It is important for individuals following the vertical diet to ensure that they are consuming a variety of foods to meet their nutrient needs. Consulting with a registered dietitian can also help individuals to ensure that they are meeting their nutrient needs while following the vertical diet.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Vertical Diet
The Vertical Diet has been gaining popularity among athletes and fitness enthusiasts in recent years. The diet is based on the principles of micronutrient sufficiency, digestive efficiency, and hormonal balance. But does it have any scientific evidence to support its claims?
Micronutrient Sufficiency
The Vertical Diet emphasizes consuming nutrient-dense foods that provide all the necessary vitamins and minerals. Research has shown that micronutrient deficiencies can lead to a range of health problems, including impaired immune function, cognitive decline, and increased risk of chronic diseases.
A study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition found that athletes who followed a micronutrient-dense diet had improved performance, reduced inflammation, and faster recovery times. The Vertical Diet's emphasis on nutrient-dense foods can help ensure athletes are getting the micronutrients they need to perform at their best.
Digestive Efficiency
The Vertical Diet also focuses on optimizing digestive efficiency by minimizing gut irritation and inflammation. This is achieved by avoiding foods that are difficult to digest, such as gluten, lactose, and high-FODMAP foods.
Research has shown that reducing gut inflammation can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. A study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that a low-FODMAP diet reduced symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome in 86% of participants.
Hormonal Balance
The Vertical Diet also aims to balance hormones by providing adequate amounts of protein, carbohydrates, and fats. Research has shown that imbalances in hormones such as insulin, cortisol, and testosterone can lead to a range of health problems, including obesity, diabetes, and infertility.
A study published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition found that a high-protein diet improved body composition and reduced cardiovascular disease risk factors in overweight and obese individuals.
Overall, while more research is needed to fully evaluate the benefits of the Vertical Diet, the scientific evidence suggests that its principles of micronutrient sufficiency, digestive efficiency, and hormonal balance may lead to improved health and athletic performance.
Who Should Consider Vertical Diet
The Vertical Diet is a dietary approach that is gaining popularity among athletes, bodybuilders, and fitness enthusiasts. While it may not be suitable for everyone, there are certain groups of people who may benefit from this diet.
Athletes and Bodybuilders
Athletes and bodybuilders require a high amount of energy to perform at their best, and the Vertical Diet provides them with the necessary nutrients to fuel their bodies. The diet includes a variety of whole foods, such as lean meats, whole grains, and vegetables, which provide the necessary protein, carbohydrates, and micronutrients needed for optimal performance.
People with Digestive Issues
The Vertical Diet is designed to be easy on the digestive system, making it a good option for people with digestive issues. The diet emphasizes easily digestible foods, such as white rice, lean meats, and low-fiber vegetables, which can help reduce digestive discomfort.
Individuals with Specific Nutritional Needs
The Vertical Diet is a flexible diet that can be tailored to meet the specific nutritional needs of individuals. For example, people who are lactose intolerant can substitute dairy products with other sources of calcium, such as leafy greens or fortified plant-based milks. Similarly, people who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet can modify the Vertical Diet to include plant-based protein sources, such as legumes and tofu.
People Who Want to Lose Weight
The Vertical Diet can be an effective weight loss tool for people who want to lose weight. The diet emphasizes whole, nutrient-dense foods, which can help reduce hunger and promote satiety. Additionally, the diet restricts processed foods and added sugars, which can contribute to weight gain.
Overall, the Vertical Diet is a dietary approach that can benefit a variety of individuals, including athletes, people with digestive issues, those with specific nutritional needs, and people who want to lose weight. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant dietary changes.
Conclusion
The Vertical Diet is a popular nutrition plan among athletes and fitness enthusiasts. It emphasizes the consumption of nutrient-dense foods and the avoidance of processed foods and allergens. The diet is designed to optimize performance, improve digestion, and support overall health.
While the Vertical Diet has its benefits, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The diet may not be suitable for individuals with specific health conditions or dietary restrictions. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new diet or exercise regimen.
In summary, the Vertical Diet is a viable option for those looking to improve their nutrition and performance. It is based on sound nutritional principles and has been shown to be effective for many individuals. However, as with any diet, it is important to tailor it to individual needs and goals, and to seek guidance from a qualified professional.
Eat well, live better!




